
"The Economics of Solar Energy: Return on Investment and Payback Periods."
Published on 14th August, 2023.
In an age marked by environmental concerns and a growing need for sustainable energy sources, solar power has emerged as a viable and attractive solution. Beyond its environmental benefits, solar energy also offers substantial economic advantages, making it a compelling choice for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. This blog explores the economics of solar energy, focusing on the concepts of return on investment (ROI) and payback periods, which play a crucial role in determining the feasibility and attractiveness of solar power investments. By examining these factors, we can unravel the financial benefits of adopting solar energy systems and understand how they contribute to a greener and economically sound future.
The Solar Revolution and Its Economic Implications.

The solar revolution signifies a paradigm shift in the way we produce and consume energy. Traditionally, our dependence on fossil fuels has led to environmental degradation, resource depletion, and geopolitical tensions. Solar energy, harnessed from the sun’s abundant rays, offers a renewable and virtually inexhaustible source of power. The advent of sophisticated photovoltaic (PV) technology has made it possible to convert sunlight directly into electricity, providing a scalable solution for both individual consumers and large-scale power plants. One of the most significant economic implications of the solar revolution is the potential for job creation and economic growth.
The solar revolution has attracted significant investment. In 2020, global investment in renewable energy, including solar, reached a record $303.5 billion, reflecting the growing confidence in the economic viability of solar power.
Return on Investment (ROI): Defining the Concept
Return on Investment, or ROI, is a fundamental financial metric used to evaluate the profitability of an investment. In the context of solar energy, ROI represents the ratio of net earnings generated by a solar system over its lifetime to the initial investment cost. Mathematically, ROI is calculated as follows:
ROI=Initial Investment Cost /Net Earnings×100
Net earnings refer to the total revenue generated from the solar system, minus any operating and maintenance costs, taxes, and other associated expenses. The initial investment cost includes the price of solar panels, inverters, installation, permits, and other setup expenses. A higher ROI indicates a more financially rewarding investment.
Factors Influencing Solar ROI
Several factors influence the ROI of a solar energy system, and understanding these variables is crucial for making informed investment decisions:
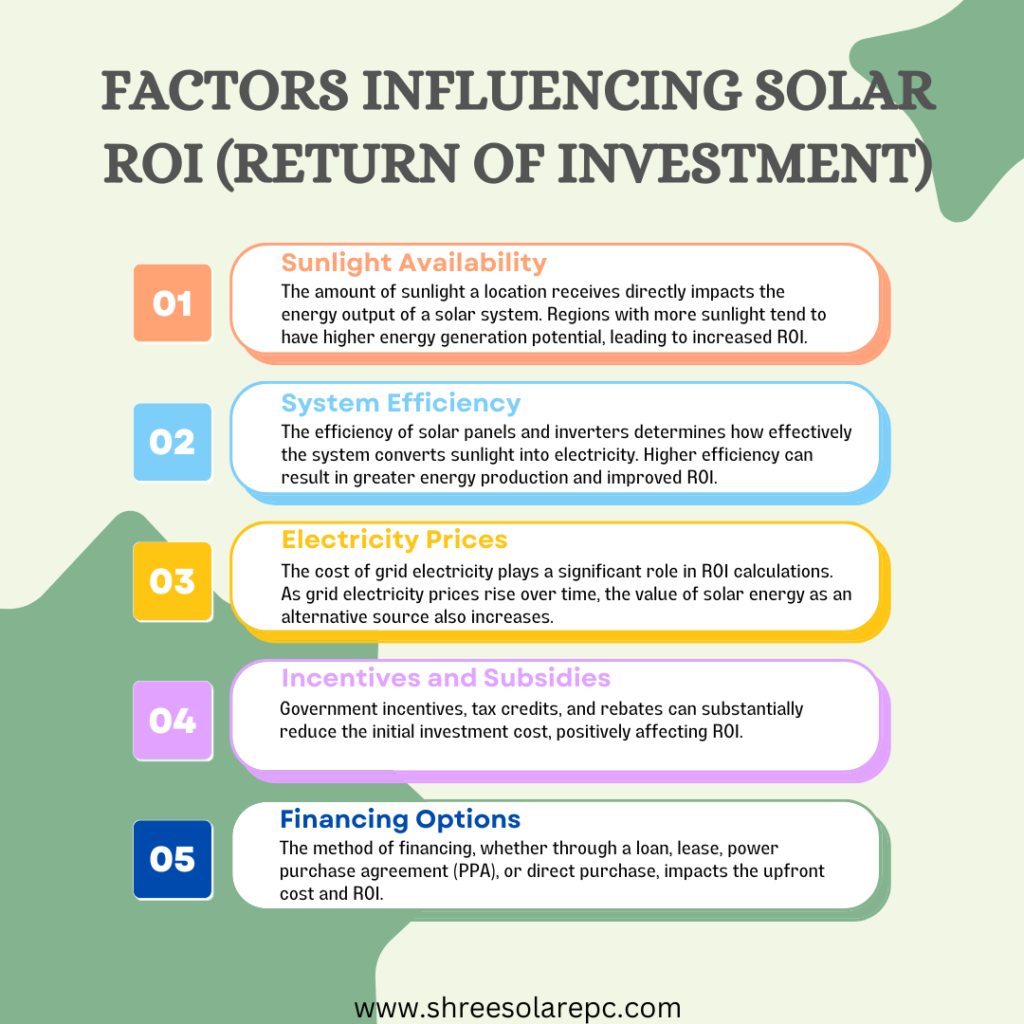
- Sunlight Availability: The amount of sunlight a location receives directly impacts the energy output of a solar system. Regions with more sunlight tend to have higher energy generation potential, leading to increased ROI.
System Efficiency and Degradation: The efficiency of solar panels and inverters determines how effectively the system converts sunlight into electricity. Higher efficiency can result in greater energy production and improved ROI. Over time, solar panels can experience efficiency degradation, resulting in reduced energy output compared to their initial performance. This gradual decline in efficiency can impact the overall ROI over the system’s lifespan.
Electricity Prices: The cost of grid electricity plays a significant role in ROI calculations. As grid electricity prices rise over time, the value of solar energy as an alternative source also increases.
Incentives and Subsidies: Government incentives, tax credits, and rebates can substantially reduce the initial investment cost, positively affecting ROI.
Financing Options: The method of financing, whether through a loan, lease, power purchase agreement (PPA), or direct purchase, impacts the upfront cost and ROI.
Payback Period: Time to Recoup the Investment
Payback period is another crucial economic indicator for solar energy investments. It represents the time it takes for the cumulative savings from a solar system to equal or exceed the initial investment cost. A shorter payback period indicates a quicker return on the investment and higher overall profitability.
Mathematically, payback period is calculated as follows:
Payback Period=Annual Savings/Initial Investment Cost
The initial investment cost includes equipment, installation, and other associated expenses. Annual savings refer to the amount of money saved on electricity bills each year due to the solar system.
Key Considerations for Payback Period
Several key factors influence the payback period of a solar energy system:
-
Upfront Costs: Lower upfront costs, often achieved through incentives or competitive pricing, can significantly reduce the payback period.
-
Energy Consumption: Higher energy consumption allows for greater savings and a potentially shorter payback period.
-
Financing Terms: The terms of financing, including interest rates for loans or lease agreements, can affect the payback period.
-
Maintenance Costs: Lower maintenance costs contribute to higher net savings, accelerating the payback period.
Making Informed Decisions: ROI vs. Payback Period
When evaluating solar energy investments, both ROI and payback period provide valuable insights. A high ROI indicates a financially attractive investment, while a short payback period offers a quicker return of the initial investment. However, the optimal balance between these two metrics depends on individual preferences and financial goals.
Some investors prioritize maximizing ROI, even if it means a longer payback period. This approach seeks higher long-term profits at the expense of waiting for a longer duration to recoup the initial investment. On the other hand, a shorter payback period may be preferred by those seeking quicker returns, even if the overall ROI is slightly lower.
Conclusion
The economics of solar energy is a complex and multifaceted subject, with return on investment and payback periods serving as crucial metrics for assessing the financial viability of solar power investments. As technology continues to advance and solar energy becomes more integrated into mainstream energy systems, understanding these economic dynamics becomes increasingly important. Whether motivated by environmental concerns, cost savings, or long-term profitability, individuals and businesses can benefit from considering the interplay between ROI and payback periods when making decisions about solar energy investments. Ultimately, solar power represents not only a sustainable energy solution but also a potentially rewarding economic endeavor.
