
"Shining Light: Solar Energy's Green Revolution For A Better Planet."
In an era characterized by rapidly depleting fossil fuel reserves, rising greenhouse gas emissions, and increasing concerns about the impact of human activities on the environment, the quest for sustainable energy sources has taken center stage. Among the various renewable energy options available, solar energy has emerged as a promising solution that not only generates power but also significantly contributes to mitigating environmental challenges. This blog explores the profound environmental impact of solar energy and how its adoption can play a pivotal role in safeguarding the planet.
The environmental impact of electricity generated using fossil fuels.
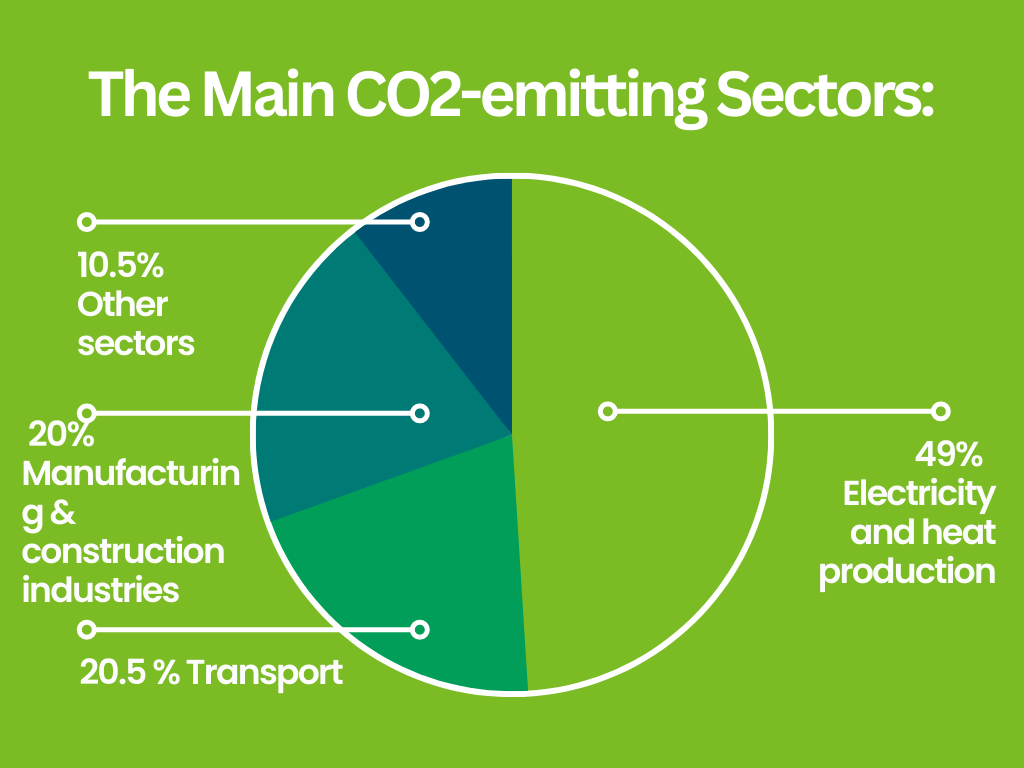
The majority of electricity generation is still heavily reliant on fossil fuels, a practice that exacts a significant environmental toll. The environmental impact of electricity generated using fossil fuels is undeniable and far-reaching, spanning from local ecological disturbances to global climate change.
Burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil and gas are the main causes of CO2 emissions. Electricity and heat production is the main sector producing almost half of total CO2 emission. As it is the main cause we need to start producing energy from renewable sources- like the SUN!
The environmental impact of generating electricity from fossil fuels is undeniable, encompassing air pollution, climate change, water resource depletion, and habitat disruption.
Environmental Benefits of Solar Energy.
1. Reduced Carbon Footprint

The carbon footprint is the total amount of greenhouse gas emissions, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), produced directly or indirectly by human activities. Fossil fuel combustion for electricity generation is a major contributor to this footprint, emitting substantial CO2 into the atmosphere and exacerbating global warming. Solar energy’s remarkable attribute lies in its ability to generate electricity with virtually zero direct CO2 emissions. By harnessing sunlight through photovoltaic (PV) panels or solar thermal systems, solar power significantly reduces the carbon footprint associated with traditional energy sources. The reduction in fossil fuel consumption, especially natural gas, has a two-fold impact. Not only does solar energy curb CO2 emissions, but it also indirectly lowers methane emissions, as methane is a potent greenhouse gas released during the extraction and transport of natural gas.
2. Mitigating Air & Water Pollution

Solar energy generation produces electricity without emitting harmful pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter. By substituting fossil fuel-based power plants, solar energy significantly diminishes the release of these pollutants into the atmosphere.
By reducing emissions that exacerbate respiratory illnesses like asthma and bronchitis, solar energy indirectly enhances public health, especially in densely populated urban areas. Unlike conventional power plants that consume vast amounts of water for cooling, solar energy systems require minimal water for operation, alleviating the strain on local water resources and reducing water pollution.
Conventional power plants release heated water into rivers and lakes, disrupting aquatic ecosystems and harming fish populations. Solar energy systems, with their limited need for cooling water, mitigate thermal pollution and help protect aquatic habitats.
3. Conserving Natural Resources.

The production of solar panels relies on materials such as silicon, which are abundant and less environmentally damaging to extract compared to fossil fuels like coal or oil. This helps conserve finite mineral resources and reduces environmental disturbance. Solar energy systems have a relatively low environmental impact during both manufacturing and operation, using minimal water and land resources compared to conventional energy sources like coal and natural gas. Solar energy systems, especially rooftop installations and solar farms on marginal lands, utilize existing infrastructure and previously underutilized spaces. This minimizes the need for land conversion and reduces pressure on ecosystems and wildlife habitats.
4. Biodiversity and Ecosystem Protection.

Conventional energy projects often necessitate large land areas, resulting in habitat destruction and fragmentation. Solar installations, especially on rooftops and marginal lands, have a significantly smaller ecological footprint, allowing ecosystems to thrive. Solar farms can be designed to incorporate native vegetation and create green spaces that support local flora and fauna. Such initiatives aid in restoring biodiversity and promoting a balanced ecosystem. Rooftop solar panels in urban areas not only generate clean energy but also provide opportunities for green spaces and vegetation, offering refuges for urban wildlife and contributing to urban biodiversity.
Solar energy stands as a beacon of hope in the global pursuit of sustainable energy solutions. Its positive impact on the environment, from reduced greenhouse gas emissions to minimized air and water pollution, underscores its vital role in safeguarding the planet for future generations. As technology advances and economies of scale continue to drive down costs, the solar revolution has the potential to reshape energy landscapes and redefine our relationship with the environment, fostering a cleaner, healthier, and more secure world for all. By embracing solar energy, we take a giant stride towards a future powered by nature’s most abundant and benevolent source – sunlight.
